In recent years, there has been a growing interest in plant-based diets, and for good reason. Along with the numerous environmental and ethical benefits, a plant-based lifestyle offers a wealth of health advantages.
At the forefront of this movement lies the power of plant-based proteins, which are not only nutritious but also incredibly versatile.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the world of plant-based proteins, their benefits, and how to seamlessly incorporate them into your daily routine.
Why Plant-Based Proteins are Gaining Popularity
Plant-based proteins have become increasingly popular due to a variety of reasons. First and foremost, they offer a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to animal-based proteins.
With rising concerns about the environmental impact of meat production, many individuals are seeking out plant-based options as a way to reduce their carbon footprint.
Additionally, plant-based proteins are often associated with a lower risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, certain types of cancer, and diabetes. This is largely due to their high fiber content, low saturated fat levels, and the absence of cholesterol.

Moreover, plant-based proteins are incredibly versatile and can be incorporated into a wide range of dishes, making them appealing to those who enjoy culinary exploration and variety in their diets.
The Ultimate Guide to Meal Prepping for Busy Weekdays
The Nutritional Powerhouse of Plant-Based Proteins
Plant-based proteins are not only delicious but also packed with essential nutrients that offer numerous health benefits. Here are some of the key advantages of incorporating plant-based proteins into your diet:
- Rich in Fibre: Many plant-based protein sources, such as beans, lentils, and whole grains, are excellent sources of fiber. Fiber is crucial for maintaining a healthy digestive system, promoting feelings of fullness, and regulating blood sugar levels.
- Low in Saturated: Fat Unlike animal-based proteins, plant-based proteins are generally low in saturated fat, which has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions.
- Packed with Antioxidants: Many plant-based protein sources, like legumes, nuts, and seeds, are rich in antioxidants. Antioxidants help protect the body’s cells from damage caused by free radicals, which can contribute to the development of various diseases.

- Abundant in Vitamins and Minerals: Plant-based proteins are often excellent sources of vitamins and minerals, such as iron, zinc, magnesium, and folate, which are essential for overall health and well-being.
Debunking 5 Common Nutrition Myths: Fact vs. Fiction
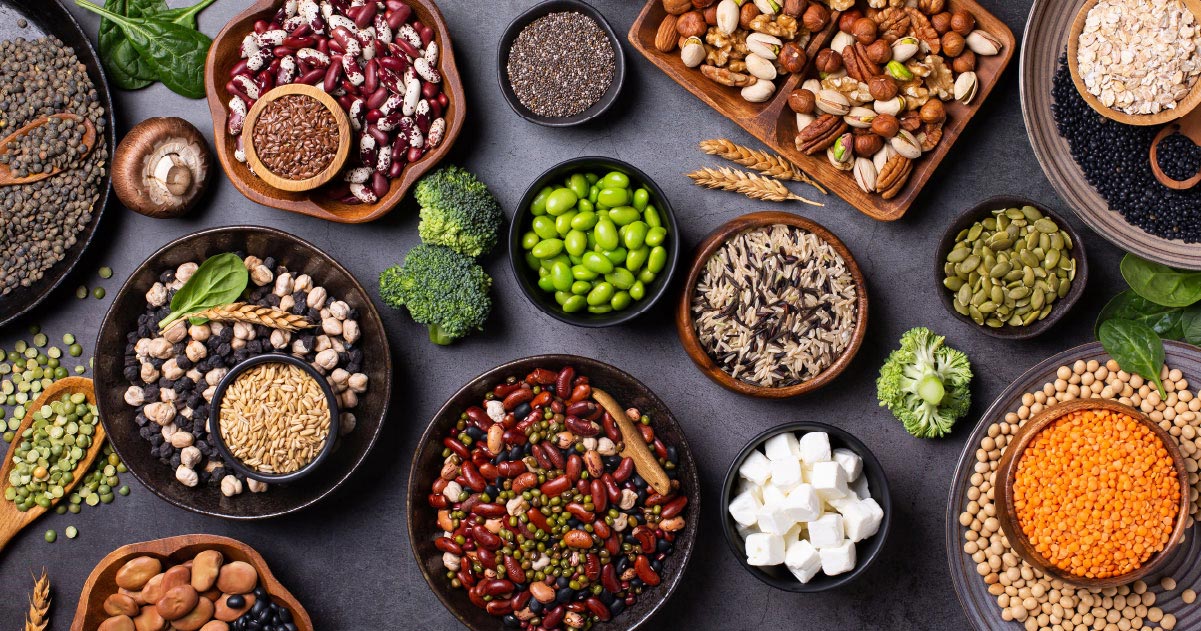
Diverse Sources of Plant-Based Proteins
One of the best things about plant-based proteins is the incredible variety of sources available. From legumes and grains to nuts and seeds, there’s something for every taste and dietary preference. Here are some of the most popular and nutritious plant-based protein sources:
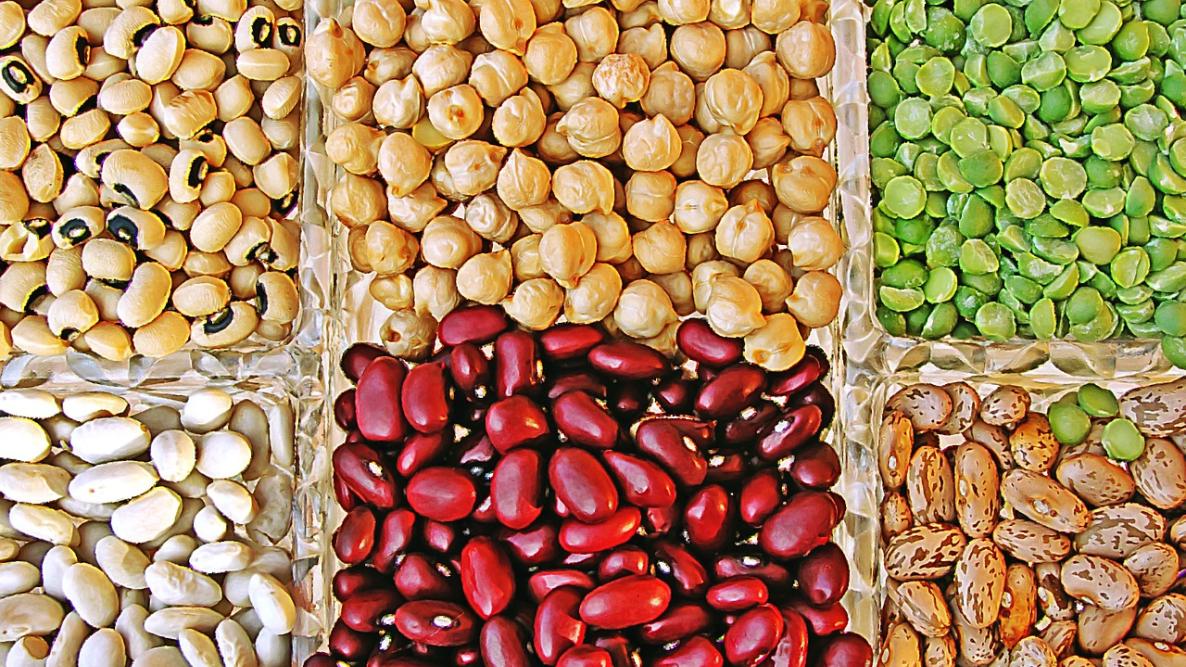
- Legumes: Legumes, such as lentils, chickpeas, peas, and beans, are among the richest sources of plant-based proteins. They’re also high in fiber, iron, and various other nutrients.

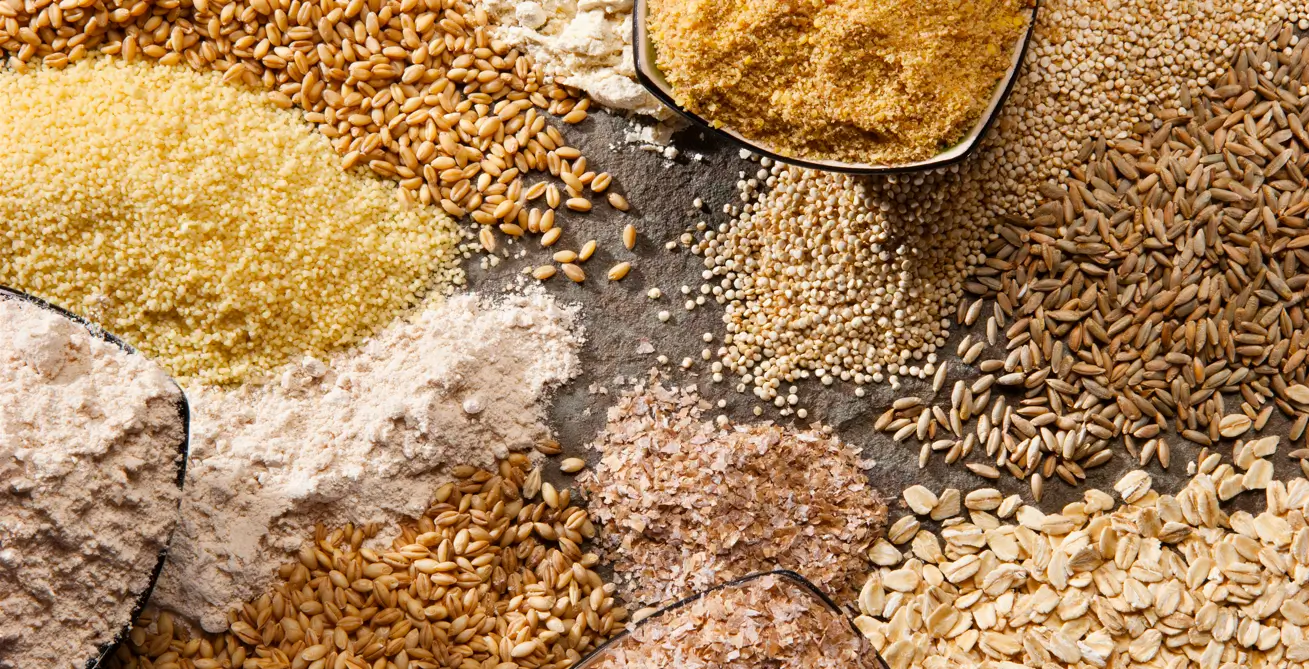
- Whole Grains: Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats are not only excellent sources of plant-based proteins but also provide a wealth of other essential nutrients, including fiber, vitamins, and minerals.

- Nuts and Seeds: Nuts and seeds, such as almonds, cashews, chia seeds, and flaxseeds, are nutrient-dense and packed with healthy fats, proteins, and a variety of vitamins and minerals.

- Soy Products: Soy-based products, including tofu, tempeh, and edamame, are rich in plant-based proteins and offer a meat-like texture, making them a popular choice for vegetarians and vegans.
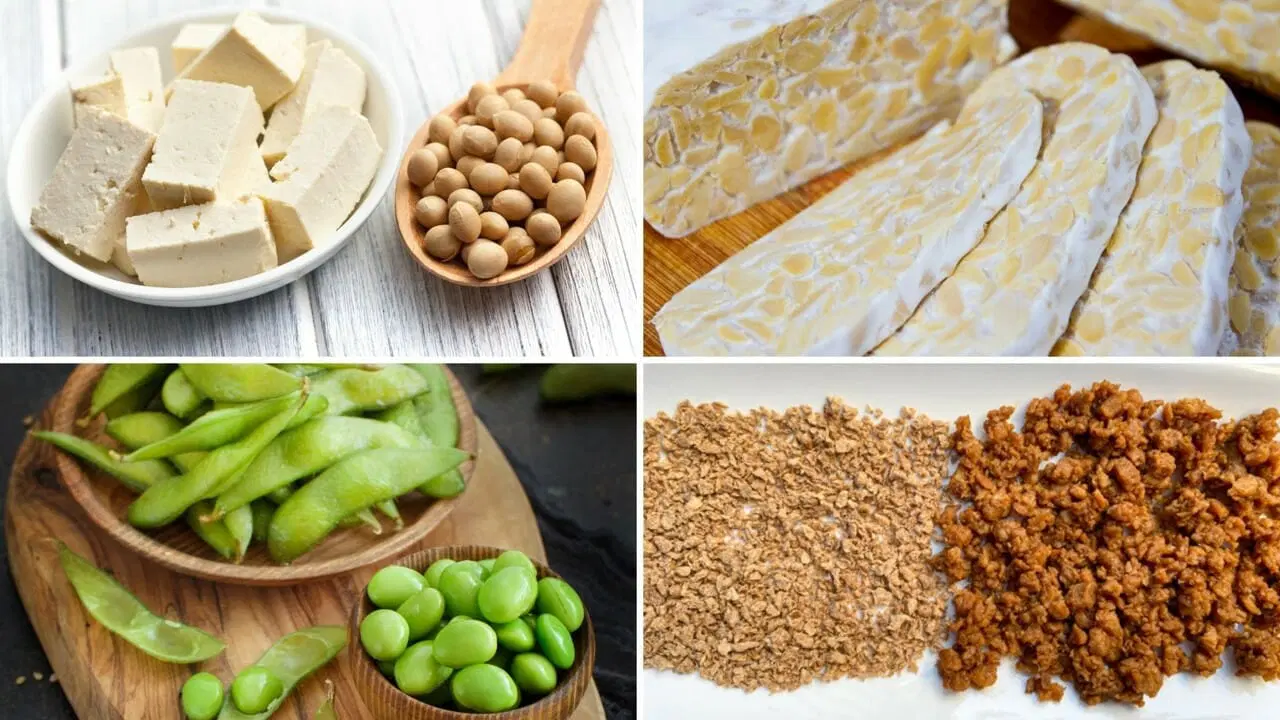

- Nutritional Yeast: Nutritional yeast is a deactivated form of yeast that’s often used as a condiment or ingredient in vegan dishes. It’s an excellent source of plant-based proteins and B vitamins, including B12, which is often lacking in plant-based diets.

Incorporating Plant-Based Proteins into Your Diet
Transitioning to a more plant-based diet doesn’t have to be overwhelming or drastic. There are numerous ways to seamlessly incorporate plant-based proteins into your daily routine:
- Swap Meat for Plant-Based Proteins: One of the easiest ways to increase your plant-based protein intake is to swap out meat for plant-based alternatives like lentils, beans, or tofu in your favorite dishes.

- Experiment with Meatless Mondays: Designate one day a week as a “Meatless Monday” and explore a variety of plant-based protein recipes. This is a great way to gradually introduce more plant-based proteins into your diet without feeling overwhelmed.
- Embrace Plant-Based Snacks: Snack on nutrient-dense plant-based proteins like nuts, seeds, or hummus with vegetables to keep you feeling full and energized throughout the day.

- Add Plant-Based Proteins to Salads and Bowls: Boost the protein content of your salads and bowls by adding legumes, quinoa, or tofu for a satisfying and nutrient-packed meal.
- Explore Meat Alternatives: There are numerous plant-based meat alternatives available on the market, ranging from veggie burgers to plant-based sausages and deli slices. These can be a great way to incorporate familiar flavors and textures into your plant-based protein routine.
Top 10 Superfoods and Their Amazing Benefits
Overcoming Challenges with Plant-Based Proteins
While transitioning to a more plant-based diet can be incredibly rewarding, there are a few potential challenges to be aware of:
- Nutrient Absorption: Some nutrients, like iron and zinc, may be less readily absorbed from plant-based sources compared to animal-based sources. However, this can be mitigated by consuming foods rich in vitamin C, which enhances the absorption of these nutrients.
- Incomplete Protein Sources: While most plant-based proteins are considered “complete,” meaning they contain all nine essential amino acids, some sources may be lacking in certain amino acids. To ensure you’re getting a complete protein profile, it’s important to consume a variety of plant-based protein sources throughout the day.

- Digestive Issues: Some individuals may experience digestive issues, such as gas or bloating when initially increasing their intake of plant-based proteins, particularly those high in fiber. This can often be alleviated by gradually introducing these foods and drinking plenty of water.
The Bottom Line
Plant-based proteins offer a wealth of health benefits and are incredibly versatile, making them an excellent addition to any diet.
By incorporating a variety of plant-based protein sources into your meals and snacks, you can enjoy a nutritious and delicious lifestyle while also supporting a more sustainable and eco-friendly future.
Whether you’re a seasoned plant-based enthusiast or just starting to explore this world, the power of plant-based proteins is truly remarkable.
References & Resources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7760812/
- https://www.heart.org/en/news/2021/08/04/eating-a-plant-based-diet-at-any-age-may-lower-cardiovascular-risk
- https://newsnetwork.mayoclinic.org/discussion/consumer-health-what-could-a-plant-based-diet-do-for-you/
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/heart-health/plant-based-fats-better-for-the-heart-than-animal-fats
- https://www.fs.usda.gov/wildflowers/ethnobotany/food/legumes.shtml